Service: IQF Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS)
Platforms
Fixlab
Techniques
Laser induced breakdown spectroscopy (libs)
Organization

Service contact persons
Phone:34913891677
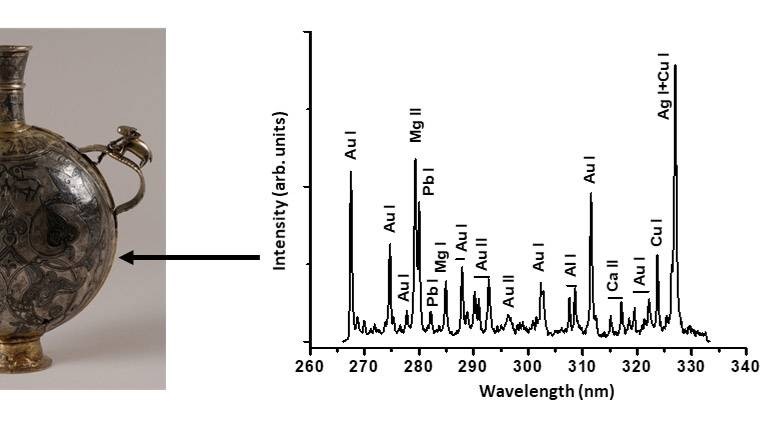
Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) is a type of atomic emission spectroscopy that uses a highly energetic laser pulse as the excitation source. The laser, focused on the material under study, generates a plasma when the laser fluence overcomes a certain threshold for optical breakdown, condition that generally depends on the environment and the target material. The spectroscopic analysis of the emitting plasma reveals the elemental composition of the sample material.
LIBS allows the characterization of the elemental composition of different materials and identification of their stratigraphies.
Fields of application
Applied physics
Archaeology
Architectural conservation
Art (discipline)
Chemistry
Decorative arts (discipline)
Heritage science (cultural heritage discipline)
Materials science
Metallurgy
Natural sciences
Materials
Organic material
Inorganic material
Inorganic pigment
Dye
Ceramic (material)
Ceramic glaze
Varnish
Glass
Metal
stone
Paper
Textiles
wood
Grisaille
Ink
Other information
-
Input: Dimensions, description of the object, previous measurements, images
-
Output: Report, individual spectra, stratigraphy profiles, spectra in *.csv