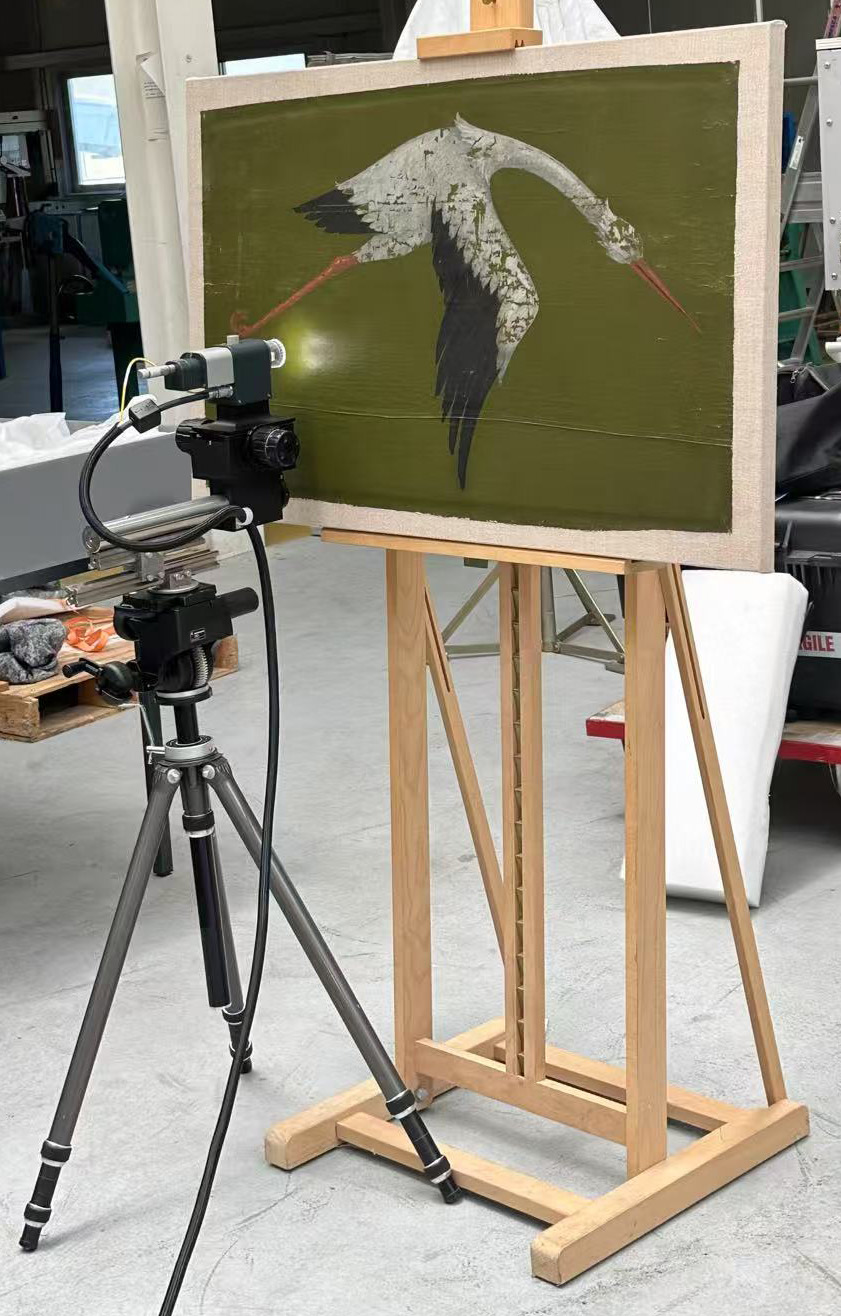
Service: OCT at 880 nm
Platforms
Molab
Techniques
Optical coherence tomography (oct)

Organization

Service contact persons
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) is an non-invasive imaging technique that uses light to capture high-resolution, cross-sectional images of translucent or transparent materials at around 880 nm. OCT is a technique that is often described as "optical ultrasound". It uses interferometry to detect light reflections within the sample, enabling detailed visualisation of internal microstructures with axial resolutions of under 10 μm. OCT is an advanced technology that can produce clear 3D reconstructions. It provides live, near-microscopic images without requiring physical contact, sample preparation, or ionizing radiation. Though its imaging depths are limited to 1–2 mm, OCT is highly valuable in cultural heritage diagnostics and research due to its safety, precision and ease of use.
Artwork Layer Structure Analysis: OCT can reveal the stratigraphy of paintings, manuscripts, and other artworks, distinguishing between varnish layers, paint, and ground layers without sampling or damaging the piece.
Varnish and Coating Inspection: It helps assessing the condition and thickness of varnishes or protective coatings on paintings or artifacts
Detection of Sub-Surface Damage: It can identify hidden cracks, voids, or degradation beneath the surface of artworks, sculptures, or ceramics, especially in translucent materials.
The materials need to be translucent or transparent around 880 nm
Fields of application
Applied physics
Heritage science (cultural heritage discipline)
Optics