Service: IQF Laser Induced Fluorescence (LIF)
Platforms
Fixlab
Techniques
Laser induced flourescence (lif)
Organization

Service contact persons
Phone:34913891677
Phone:34917459515
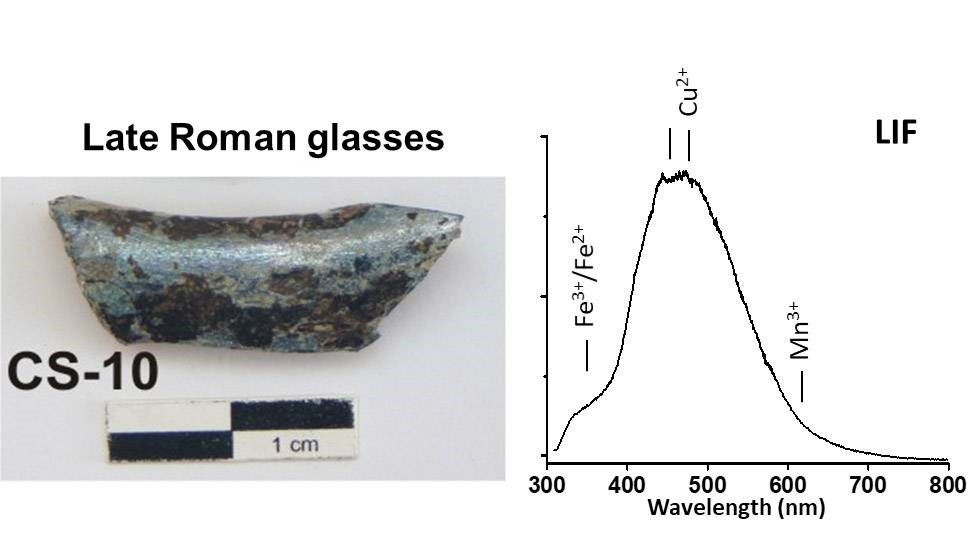
Laser-induced fluorescence (LIF) is a non-invasive spectroscopic method in which the atoms or molecules of a sample are excited to a higher energy level by the absorption of laser photons followed by spontaneous emission of light. Spectroscopic analysis of the emitting light provides information of the molecular composition of the target material.
LIF uses UV photons for material excitation in order to get spontaneous fluorescence emission informing on its structural composition.
Fields of application
Applied physics
Archaeology
Architectural conservation
Art (discipline)
Chemistry
Decorative arts (discipline)
Heritage science (cultural heritage discipline)
Materials science
Natural sciences
Materials
Combination inorganic/organic material
Gum (material)
Inorganic material
Organic material
Varnish
stone
Pigments
Binding media
Biopolymers
Polymers
Glass
Gelatin
Grisaille
Paintings
Methods
Other information
-
Input: Dimensions, description of the object, previous measurements, images.
-
Output: Report, individual spectra, molecular maps, spectra in *.csv.