Service: UV-VIS-NIR Fluorescence spectroscopy
Platforms
Molab
Techniques
Uv-vis-nir fluorescence spectroscopy

Organization

Service contact persons
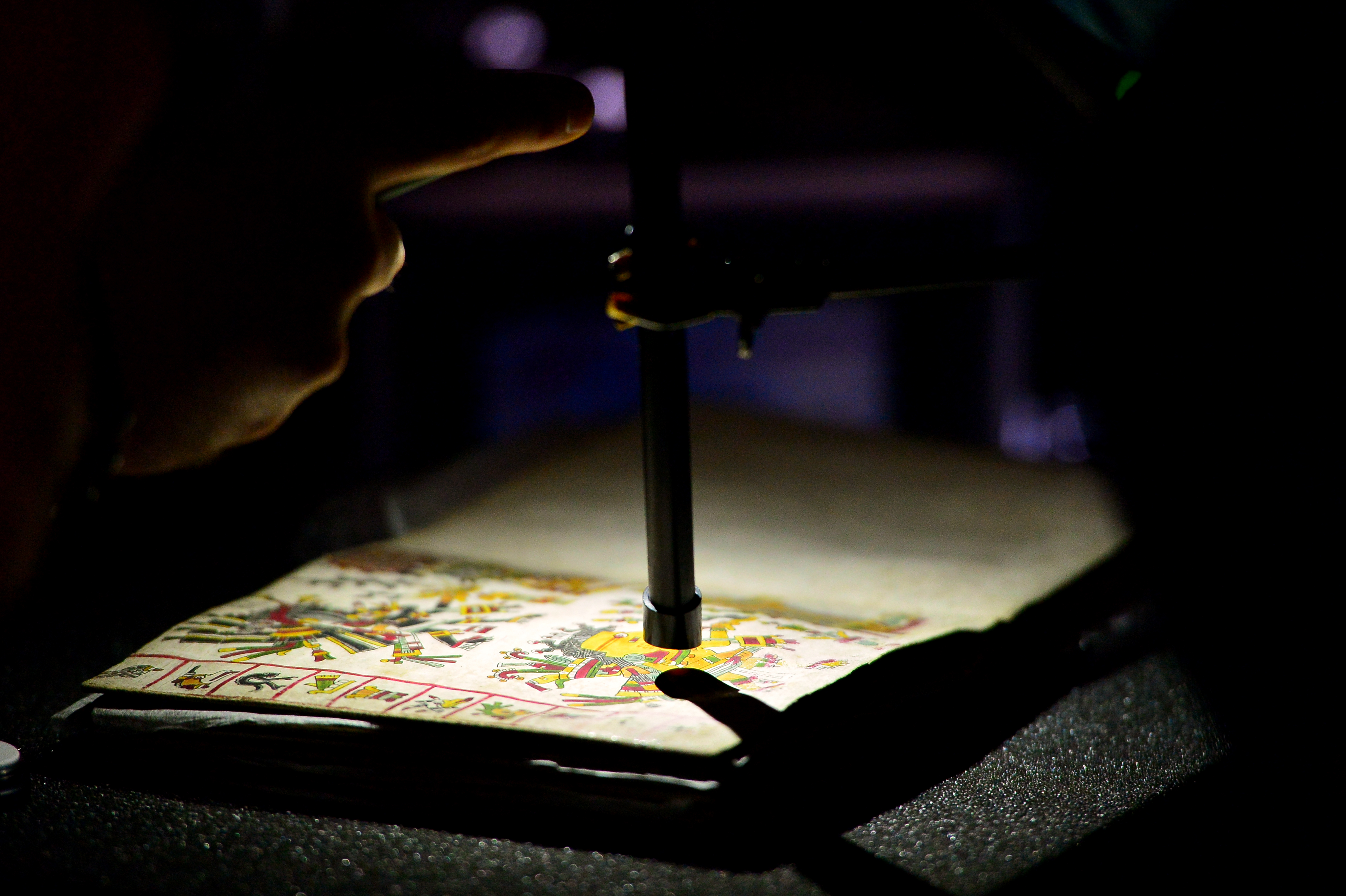
UV-VIS-NIR fluorescence spectroscopy is a non-invasive technique suitable for the identification of different organic and inorganic materials (pigments and dyes) in artworks.
The absorption of an electromagnetic radiation promotes the population of an excited electronic state of a molecular species. This excited state rapidly dissipates its energy and this phenomenon can happen via a so-called radiative pathway, producing characteristic emission of photons in the UV-VIS-NIR spectral ranges, commonly called fluorescence. The fluorescence measurements are particularly indicated for the characterization of several organic dyes as well as luminescent pigments such as zinc oxide, cadmium based pigments and Egyptian blue.
Fields of application
Archaeology
Archaeometry
Art (discipline)
Art history
Conservation (discipline)
Conservation science (cultural heritage discipline)
Heritage science (cultural heritage discipline)
Preventive conservation
Materials
Pigments
dyes
minerals
Pigments
dyes
minerals
Other information
-
Input: Imaging/photografic (Vis, UV, NIR) documentation available from the users (jpg, tiff)
-
Output: Original Ascii files; report, metadata (experimental conditions, comments relative to the point), data interpretation; image of the sampling area